For some background, I would like to turn your attention to a study from Mohammed et. al , which states that video game addiction can lead to changes in the brain that are similar to brain activity of those addicted to substances and gambling. This can lead to negative psychological changes in teenagers and children whose brain is still in development. Hence you as a designer need to proceed with caution. Is profit over the health of the people within society worth it?
According to Karhulahti there are multiple different frameworks which are called vitality structures to bond technology and the human experience. One of them is called CLIMB and this is the feeling of progressing according to the amount of effort the player has exerted. This can be experienced, such as leveling up in games or ranking systems. Which in ranking systems, players most of the time unable to consecutively win and rank up. This can cause their progress to slow and increase the amount of time they need to spend on the game. Noted in the paper, often when a player wins a visual animation is played which makes a positive visual association with winning versus not showing the same downward movement when a loss occurs.
Another element is called FINAL STRETCH where there is an unfulfilled goal that is within reach that elicits the feeling of "I should complete it" versus it just being close to completion. Such as needing one more win to rank up or collecting an item in order to progress in the game
The last element is called ALERT, this refers to an ephemeral feeling that a player gets when they become aware of this alert. This could be a form of conditioning that elicits a positive response to this ALERT. Such as a notification for an event or something else that needs to be completed in the game to prompt a player to return.
Xiao and Henderson explains how loot box pricing that uses virtual currency that must be purchased with actual money can be deceptive, since it conceals the actual cost of the loot boxes. This can lead to many microtransactions, which are small monetary transactions for in game loot. The player oftentimes will not realize how much money they are spending on the game.
Using this information to design non-addictive games is essential to protecting teenagers and those susceptible to gambling.
How can you reduce these microtransactions or at least make the player aware of how much they are spending? How can you encourage playing, but not to the point where it is detrimental?
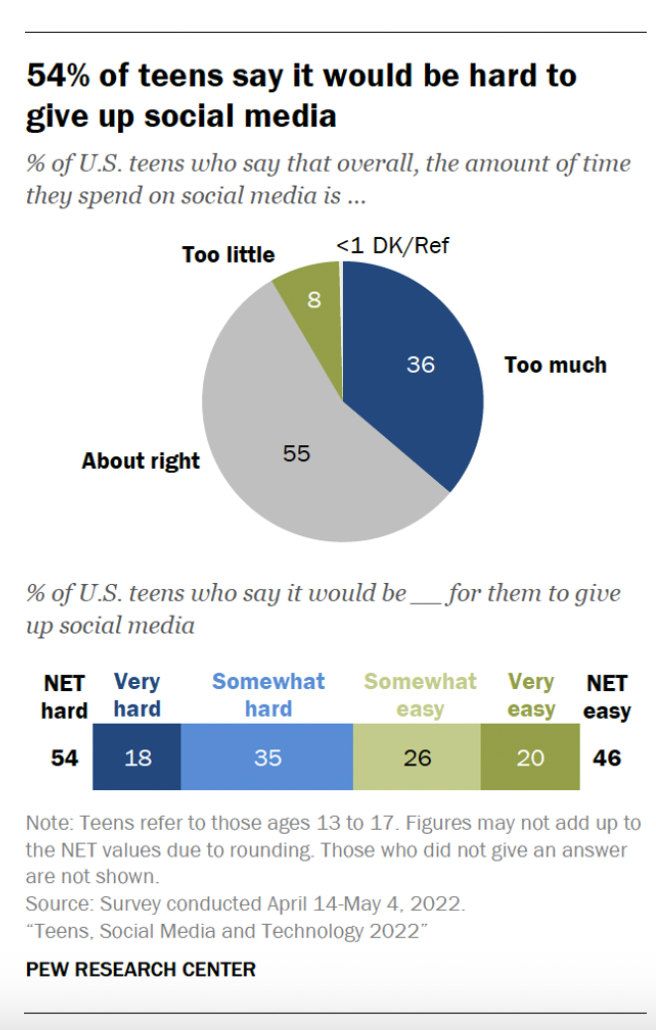
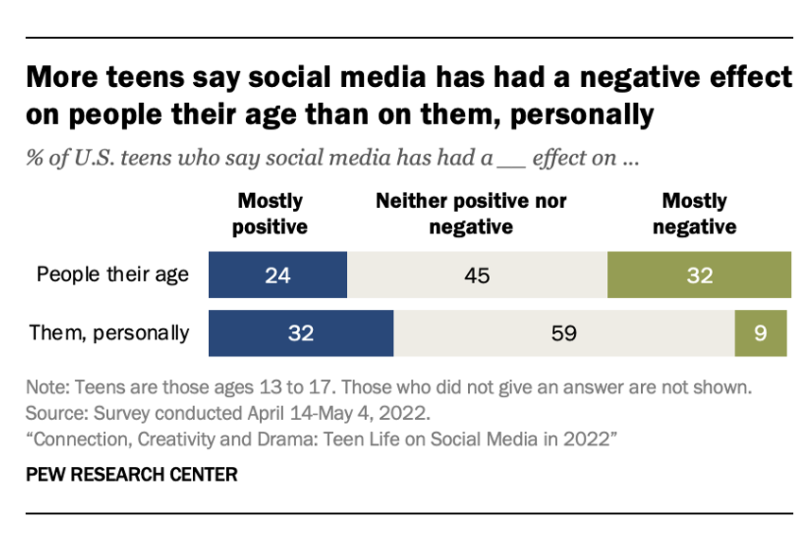
According to the statistics on the graphs shown, teenagers often think 32% of others their age are being negatively affected by social media, however when they report about themselves, only 9% believe they are being affected negatively. With 54% of teenagers citing it would be difficult for them to give up social media, along with 36% of them saying they use it too much.


This article The Addictiveness of Social Media:How Teens Get Hooked explains how social media is easily addictive and can cause those who use social media excessively to develop issues with their mental health. Some include low self-esteem, eating disorders, and suicidal thoughts.
Social media can cause stimulating effects that are similar to an addiction, this works by triggering dopamine surges. This occurs when a user gets notificaions about shares, likes, and comments on their posts. This elicits a positive feeling for the user, which then conditions the user to seek out more of these positive feelings through social media use.
Some users such as teenagers are especially susceptible due to adolescence being a large period of brain growth, which overusing social media can have an actual effect on this growth and cause the brain to seek immediate gratification.
Data and visuals from the Pew Research Center. Image Source: Emily A. Vogels and Risa Gelles-Watnick, 2023. Accessed via the Pew Research Center website